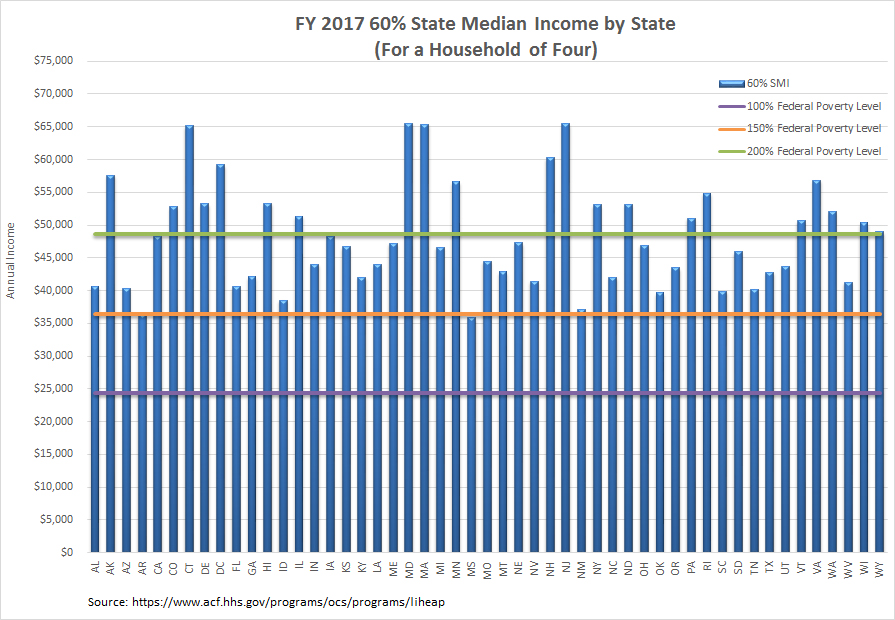
July 8, 2016—Earlier this week, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) released the updated guidelines for the state median income (SMI) to be used for Fiscal Year 2017. SMI is one of the income criteria that LIHEAP grantees can use in determining household eligibility.
Derived from the U.S. Census Bureau's "American Community Survey," the new SMI figures become effective any time between their publication date and either October 1, 2016 (the beginning of the 2017 federal fiscal year) or the beginning of a grantee's 2017 fiscal year, whichever occurs later. According to LIHEAP regulations, grantees can establish the maximum household income for LIHEAP eligibility at either 150 percent of federal poverty guidelines or 60 percent of SMI. During FY 2016, 17 states and the District of Columbia used 60 percent of SMI for their LIHEAPs.
While SMI can be used to set income eligibility for LIHEAP, it also shows the disparity in income across the country. The chart below of SMI for FY 2017 reveals that the top state has a median income that almost doubles that of the bottom state.